Which Type of Headache Has Less of a Tendency to Run in Families?
A cluster headache is an uncommon type of headache. It is one-sided head pain that may involve tearing of the eyes, a droopy eyelid, and a stuffy olfactory organ. Attacks last from 15 minutes to three hours, occur daily or almost daily for weeks or months. The attacks are separated by pain-free periods that last at least 1 month or longer.
Cluster headaches may be confused with other mutual types of headaches such as migraines, sinus headache, and tension headache.
Doctors practice not know exactly what causes cluster headaches. They seem to be related to the body'southward sudden release of histamine (chemic in the trunk released during an allergic response) or serotonin (chemical made by nerve cells) in the area of a nerve in the face called the trigeminal nerve. A problem in a small area at the base of operations of the encephalon chosen the hypothalamus may be involved.
More men than women are affected. The headaches can occur at any age, but are most common in the 20s through middle age. They tend to run in families.
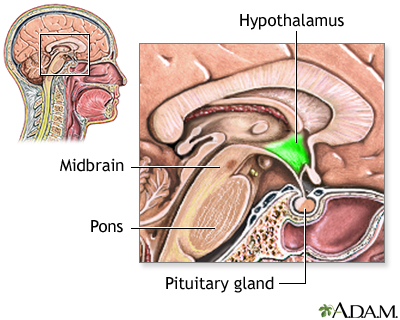
Cluster headaches may be triggered by:
- Alcohol and cigarette smoking
- High altitudes (trekking and air travel)
- Brilliant light (including sunlight)
- Exertion (concrete activity)
- Heat (hot weather or hot baths)
- Foods high in nitrites (bacon and preserved meats)
- Certain medicines
- Cocaine
A cluster headache begins as a astringent, sudden headache. The headache commonly strikes 2 to 3 hours afterward y'all fall asleep. But it tin too occur when you are awake. The headache tends to happen daily at the same time of day. Attacks can last for months. They can alternating with periods without headaches (episodic) or they can go on for a year or more without stopping (chronic).
Cluster headache pain is usually:
- Burning, sharp, stabbing, or steady
- Felt on i side of the face from neck to temple, often involving the center
- At its worst within five to x minutes, with the strongest pain lasting 30 minutes to 2 hours
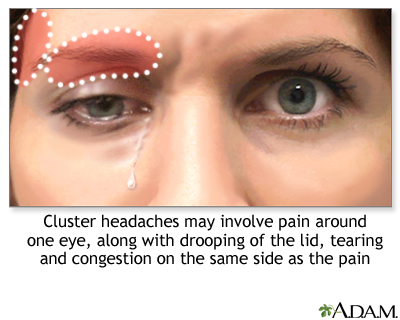
When the centre and nose on the same side as the head hurting are afflicted, symptoms can include:
- Swelling under or effectually the eye (may touch on both eyes)
- Excessive tearing
- Red centre
- Droopy eyelid
- Runny nose or stuffy nose on the aforementioned side as the caput pain
- Ruby-red, flushed face, with extreme sweating
Your health care provider can diagnose this type of headache by performing a concrete exam and asking most your symptoms and medical history.
If a physical exam is done during an attack, the exam will unremarkably reveal Horner syndrome (one-sided eyelid drooping or a minor pupil). These symptoms will not be present at other times. No other nervous system (neurologic) changes will exist seen.
Tests, such as an MRI of the head, may exist needed to rule out other causes of the headaches.
Treatment for cluster headaches involves:
- Medicines to treat the hurting when information technology happens
- Medicines to forestall the headaches
TREATING CLUSTER HEADACHES WHEN THEY OCCUR
Your provider may recommend the post-obit treatments for when the headaches occur:
- Triptan medicines, such as sumatriptan (Imitrex).
- Anti-inflammatory (steroid) medicines such as prednisone. Starting with a high dose, then slowly decreasing information technology over ii to 3 weeks.
- Breathing in 100% (pure) oxygen.
- Injections of dihydroergotamine (DHE), which can terminate cluster attacks within 5 minutes (Warning: this drug tin be dangerous if taken with sumatriptan).
Y'all may need more one of these treatments to control your headache. Your provider may have you attempt several medicines before deciding which works best for you.
Pain medicines and narcotics do not unremarkably relieve cluster headache hurting considering they take as well long to work.
Surgical treatment may exist recommended for yous when all other treatments take failed. One such treatment is a neurostimulator. This device delivers tiny electrical signals to certain nerves such as the occipital nerve in the scalp. Your provider tin can tell yous more about surgery.
PREVENTING CLUSTER HEADACHES
Avoid smoking, booze use, certain foods, and other things that trigger your headaches. A headache diary can help you identify your headache triggers. When you get a headache, write downwards the post-obit:
- Day and time the hurting began
- What y'all ate and drank over the past 24 hours
- How much you slept
- What you were doing and where you were right before the pain started
- How long the headache lasted and what fabricated it cease
Review your diary with your provider to place triggers or a design to your headaches. This tin can assist you and your provider create a treatment plan. Knowing your triggers tin can help you avoid them.
The headaches may go away on their own or you lot may need treatment to prevent them. The following medicines may also be used to treat or preclude headache symptoms:
- Allergy medicines
- Antidepressants
- Claret force per unit area medicines
- Seizure medicine
Cluster headaches are not life threatening. They unremarkably do non cause permanent changes to the brain. Merely they are long-term (chronic), and often painful enough to interfere with work and life.
Call 911 if:
- You are experiencing "the worst headache of your life."
- You have speech, vision, or movement issues or loss of balance, particularly if yous accept not had these symptoms with a headache before.
- A headache starts suddenly.
Schedule an appointment or call your provider if:
- Your headache blueprint or hurting changes.
- Treatments that once worked no longer help.
- You accept side effects from your medicine.
- You lot are pregnant or could become pregnant. Some medicines should not be taken during pregnancy.
- You need to have pain medicines more than 3 days a week.
- Your headaches are more severe when lying down.
If y'all smoke, now is a expert fourth dimension to stop. Booze use and whatsoever foods that trigger a cluster headache may need to be avoided. Medicines may prevent cluster headaches in some cases.
Histamine headache; Headache - histamine; Migrainous neuralgia; Headache - cluster; Horton's headache; Vascular headache - cluster; Episodic cluster headache; Chronic cluster headache
Garza I, Schwedt TJ, Robertson CE, Smith JH. Headache and other craniofacial hurting. In: Daroff RB, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, eds. Bradley'southward Neurology in Clinical Do. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 103.
Hoffmann J, May A. Diagnosis, pathophysiology, and management of cluster headache. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(ane):75-83. PMID: 29174963 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29174963.
Rozental JM. Tension-type headache, chronic tension-type headache, and other chronic headache types. In: Benzon HT, Raja SN, Liu SS, Fishman SM, Cohen SP, eds. Essentials of Pain Medicine. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap xx.
Updated by: Alireza Minagar, Medico, MBA, Professor, Department of Neurology, LSU Wellness Sciences Center, Shreveport, LA. As well reviewed by David Zieve, Doctor, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.Chiliad. Editorial team.
Source: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000786.htm
0 Response to "Which Type of Headache Has Less of a Tendency to Run in Families?"
Post a Comment